Endotracheal intubation is an essential basic skill in first aid and anesthesia operations, especially in emergency situations, being able to perform endotracheal intubation quickly and accurately often determines the life and death of patients. For medical students, mastering this skill is key to entering clinical practice. Advanced tracheal intubation training model, as a high simulation teaching tool, is providing students with a risk-free, efficient and professional training environment, helping them reduce mistakes in practical operation and improve clinical skills.
Teaching model: high degree of imitation, intuitive operation
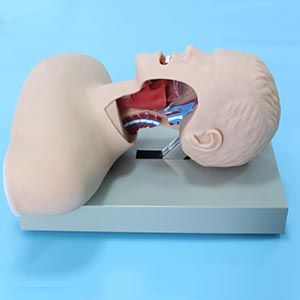
Advanced tracheal intubation training mode
The advanced Tracheal intubation training model accurately simulates the human airway structure, including the mouth, larynx and trachea, through highly simulated design. Through repeated practice with the model, students experience the entire process from pre-intubation airway assessment to successful intubation. Compared with the real person simulation, the training model provides a more flexible operating space, and the trainees can practice many times without the pain or discomfort of the patients, and truly achieve technical proficiency and confidence.
In addition, the model provides a detailed feedback mechanism to monitor the quality of the intubation operation in real time and help students adjust the method of operation in real time. This direct, immediate feedback is essential for students to master proper intubation techniques and avoid common misintubation.
Personal skills: Refine your skills through repeated practice
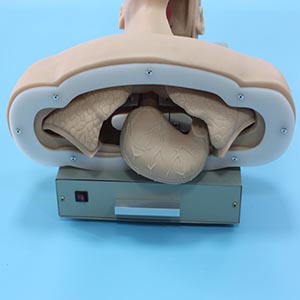
The master of tracheal intubation technology needs to accumulate a lot of practice and meticulous skills. The advanced Tracheal intubation training model provides students with plenty of practice opportunities to help them gradually improve their skills in a simulated environment. Not only can students practice the correct Angle, force and depth of intubation, but they can also experience how to deal with various emergencies, such as airway obstruction and reactions that occur during the procedure.
Through model training, students can be familiar with and master every detail of tracheal intubation, reducing the risk caused by improper operation in clinical practice. After repeated training, the trainees' operational fluency and emergency response ability have been significantly improved, laying a solid foundation for entering clinical practice and subsequent first aid work.
Data support: Evidence of increased skill success
Research data show that using advanced tracheal intubation training model can significantly improve students' skill mastery and intubation success rate. One study found that medical students who underwent simulated training improved the success rate of intubation in actual clinical operations by about 25%. Another survey showed that through repeated training, students' error rate in tracheal intubation was reduced by more than 30%.
This efficient training results from the model's high fidelity and detailed feedback mechanism, which allows students to identify problems and adjust techniques with each exercise, thereby continuously improving their skills. The data also showed that students trained with the advanced model were generally able to complete high-quality intubation operations in less time, reducing unnecessary time wastage and patient risk in the emergency scene.
Professional recognition: an essential tool for improving clinical skills
Experts generally believe that the advanced tracheal intubation training model is an important tool in medical education. It not only helps students improve their intubation skills, but also helps them develop the ability to deal calmly in emergency situations. Medical experts pointed out that through simulation training, students can complete the intubation more confidently and accurately when they encounter the actual operation, reducing the harm and discomfort to patients.
Overall, the advanced Tracheal intubation training model provides medical students with a practical and theoretical training platform that enables them to master this critical skill through repeated practice without patient pressure. Supported by data and highly recognized by experts, this training tool is becoming an integral part of medical education and first aid training.