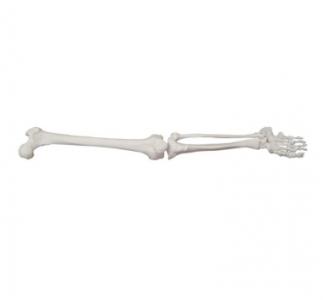
The large lower limb bone model plays an indispensable role in medical education to improve medical skills. With its unique advantages, this model provides medical students and medical professionals with a platform for in-depth understanding and practice of lower limb skeletal anatomy, thus significantly promoting the improvement of medical skills.
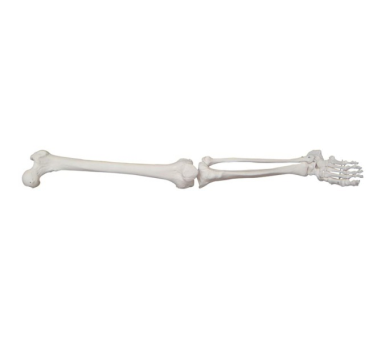
First of all, the large lower limb skeleton model accurately reproduces the complex structure of the human lower limb skeleton through its highly simulated design. From the main bones such as the femur, tibia and fibula, to the joint connections between them, ligament attachments and muscle start and end points, the model is shown in detail. This intuitive and touchable learning method enables medical students to quickly establish three-dimensional cognition of the skeletal system of human lower limbs, laying a solid foundation for subsequent medical practice.
Secondly, the large lower limb bone model provides valuable practical operation opportunities for medical students. On the model, students can simulate surgical operations such as fracture reduction and joint replacement, which not only helps them to familiarize themselves with the surgical process, but also exercises their hand-eye coordination and fine manipulation skills in practice. In addition, the detachable design of the model allows students to gain insight into the internal structure of bones and joints, further deepening their understanding of anatomy.
In addition, the large lower limb bone model also plays a role as a teaching aid in the process of medical skill improvement. Teachers can use models for vivid teaching demonstrations, and teach complex anatomical knowledge to students in an intuitive and understandable way. At the same time, students can also deepen their memory and understanding of knowledge points by observing, touching and discussing various structures on the model. This interactive teaching method not only improves students' learning interest and enthusiasm, but also promotes the exchange and communication between teachers and students.
Finally, the large lower limb bone model also provides students with an opportunity for self-assessment and reflection. After completing the practical operation, students can check whether their operation is correct and whether the expected effect is achieved against the model. This process of self-assessment helps students to identify and correct their own mistakes in time, so as to continuously improve their medical skills.
To sum up, the large lower limb skeletal model plays an important role in medical education. It not only provides students with an intuitive and touchable learning platform, but also provides them with valuable practical operation opportunities and teaching AIDS. By making full use of this model for study and practice, medical students can continuously improve their medical skills and be fully prepared for future medical work.